In a world increasingly aware of environmental impact, eco-friendly gardening is not just as a trend, but as a vital practice in nurturing our planet. As gardeners, our choices can profoundly influence local wildlife, water usage, and the chemical balance of our soil—echoing beyond our own backyards to the broader environment. At Rolling Fields Tree Farm, we understand the power of responsible gardening and are committed to practices that support a healthier Earth.
Eco-friendly gardening involves more than just planting—it's about creating a sustainable ecosystem that promotes biodiversity and sustainability. By choosing the right plants, utilizing natural resources wisely, and reducing reliance on harmful chemicals, we can cultivate spaces that are not only beautiful but also beneficial to the environment. This approach not only conserves vital resources but also offers a sanctuary for local fauna and flora, enhances air quality, and ensures that our green spaces contribute positively to our surroundings.
Join us as we explore how every gardener can implement sustainable practices that make a difference, turning each green space into a vibrant, eco-friendly haven.

1. Understanding Eco-Friendly Gardening
Eco-friendly gardening is more than just a way to beautify your space—it's a method of cultivation that aligns with the rhythms of nature rather than working against them. This approach to gardening is designed to minimize both waste and impact, using techniques that support a natural ecological balance and foster biodiversity.
Key Components of Eco-Friendly Gardening:
Sustainability: This principle focuses on using resources in a way that does not deplete them for future generations. It includes practices like rainwater harvesting and using renewable energy sources.
Organic Practices: Avoiding synthetic chemicals and fertilizers, eco-friendly gardening relies on organic compost, natural pest control, and heirloom seed varieties which are more resilient and adaptable to local conditions.
Wildlife Support: Eco-friendly gardens also play a crucial role in supporting local wildlife. By planting native species and creating habitats, gardens can become a refuge for beneficial insects, birds, and other wildlife.
Benefits to Gardeners and the Environment:
Reduced Chemical Use: By avoiding harsh chemicals, you contribute to healthier soil and groundwater, which positively impacts local water quality and wildlife health.
Increased Biodiversity: Eco-friendly gardens help to attract and sustain a variety of species, contributing to the ecological health of the area.
Enhanced Beauty and Productivity: Naturally maintained gardens are vibrant and productive, offering a lush, healthy environment that supports both plant and animal life.

2. Choosing the Right Plants
Selecting the appropriate plants is foundational to establishing an eco-friendly garden. Choosing native species not only supports the local ecosystem but also minimizes the need for water, fertilizers, and pesticides. Native plants are naturally adapted to their environment, making them more resilient and easier to care for.
Benefits of Native Plants:
Water Conservation: Native plants require less water once established, as they are adapted to the local climate and soil conditions.
Lower Maintenance: They generally require less upkeep due to their natural adaptation to the environment.
Support for Local Wildlife: Native plants provide essential habitats and food sources for local wildlife, promoting biodiversity.
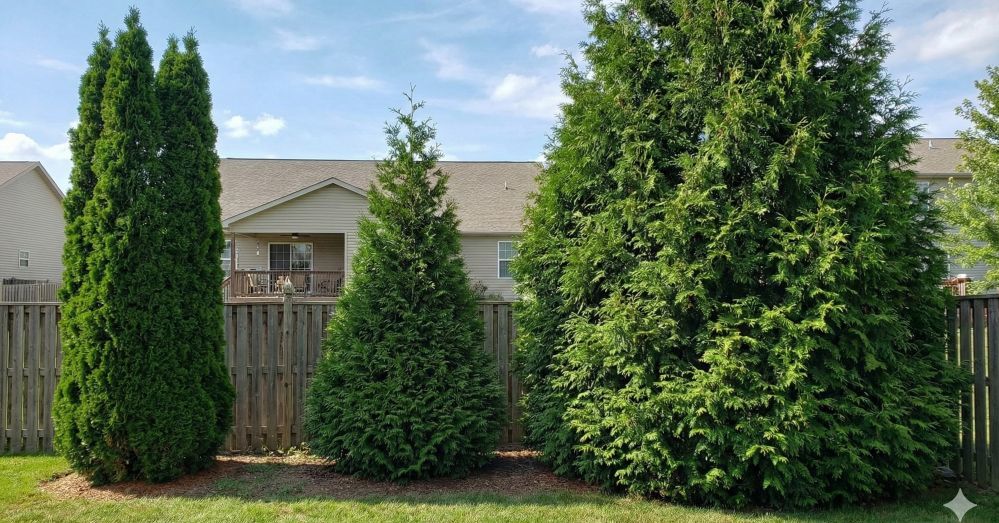
Including Arborvitae in Your Garden:
Privacy and Beauty: The arborvitae, particularly varieties like the Green Giant, offer lush, evergreen foliage that is perfect for creating natural privacy screens.
Eco-Friendly Benefits: Arborvitae trees are known for their hardiness and low maintenance needs. They grow quickly, providing substantial benefits such as windbreaks and noise reduction, while requiring minimal care.
Versatility: Suitable for various landscape designs, arborvitae can be used in formal gardens, windbreaks, or as standalone features.

3. Soil Health and Management
Healthy soil is the cornerstone of any garden, especially one that aims to be sustainable. Ensuring that your soil is rich in nutrients and alive with microorganisms not only supports plant health but also enhances the garden's ability to maintain ecological balance without chemical interventions.
Techniques for Improving Soil Fertility Naturally:
Composting: Adding compost is one of the most effective ways to enrich your soil. Compost provides a wealth of nutrients and encourages beneficial microbial activity that helps break down organic material into vital plant nutrients.
Mulching: Applying mulch helps retain soil moisture, suppress weeds, and improve soil quality as it decomposes. Organic mulches like bark, straw, or leaf litter also add nutrients back into the soil as they break down.
Avoiding Chemical Fertilizers and Pesticides:
Organic Alternatives: Instead of synthetic fertilizers, opt for organic options that release nutrients slowly, improving soil health over time without the risk of chemical runoff.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM): This approach involves monitoring the garden for pests and choosing control methods that are least disruptive to the environment, such as biological control, mechanical barriers, or natural pesticides.
Role of pH and Soil Testing:
Understanding Soil pH: Knowing the pH of your soil is crucial as different plants thrive in different pH levels. Adjusting the pH naturally through amendments like sulfur or lime can help create the ideal growing environment.
Regular Soil Testing: Testing your soil every few years can provide valuable insights into its nutrient content and overall health, guiding your amendment and fertilization choices more accurately.

4. Water Conservation Strategies
Water is a precious resource, and conserving it is a key aspect of eco-friendly gardening. Efficient water use not only saves this vital resource but also supports a healthy garden by preventing overwatering and reducing runoff, which can carry pollutants into local waterways.
Installing Drip Irrigation Systems:
Efficiency: Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff. It's an efficient system that can save up to 50% more water than traditional watering methods.
Customization: These systems can be customized to the specific needs of each plant, ensuring they receive the right amount of water without waste.
Best Practices for Water-Efficient Gardening:
Watering Times: Water early in the morning or late in the evening to reduce water loss through evaporation during the hotter parts of the day.
Watering Depth: Water less frequently but deeply to encourage deep root growth, which makes plants more drought-resistant.
Mulching: As mentioned, mulching conserves water by retaining soil moisture and reducing the need for frequent watering.
Utilizing Rainwater:
Rain Barrels: Installing rain barrels is an excellent way to harness natural rainfall. This collected water can be used for watering the garden, further reducing your dependency on municipal water systems.
Rain Gardens: Creating rain gardens can help manage stormwater runoff, reducing erosion and water pollution while providing a water-efficient, beautiful landscape feature.

5. Utilizing Organic and Natural Pest Control
An integral part of eco-friendly gardening involves managing pests without relying on harsh chemical pesticides, which can harm beneficial insects, birds, and the environment. Using organic and natural methods for pest control not only keeps your garden healthy but also maintains the ecological balance, supporting biodiversity.
Introduction to Integrated Pest Management (IPM):
IPM Overview: This strategy involves using the least toxic methods first, such as cultural, mechanical, and biological controls, and resorting to chemicals as a last resort.
Monitoring: Regularly inspecting your garden for pest activity helps in early detection, which is key to effective management.
Examples of Natural Pest Repellents and Beneficial Insects:
Natural Repellents: Garlic spray, neem oil, and soap sprays can deter a variety of pests without harming plants or beneficial organisms.
Attracting Beneficial Insects: Planting flowers like marigolds, sunflowers, and herbs can attract beneficial insects like ladybugs, bees, and lacewings that prey on harmful pests.
Creating Barriers and Traps:
Physical Barriers: Using netting or row covers to protect plants from insects and birds can be very effective.
Traps: Pheromone traps or sticky traps can catch and reduce the numbers of pests without using chemicals.
Promoting Natural Predators:
Birds, Bats, and Frogs: Encouraging these natural predators into the garden can help control pest populations naturally. Birdhouses, bat boxes, and small ponds can make your garden more attractive to these allies.

6. Promoting Pollinators
Pollinators play a crucial role in the health of natural ecosystems and the production of fruits and vegetables in our gardens. By creating a pollinator-friendly garden, you contribute to the conservation of these essential creatures, which include bees, butterflies, birds, and other insects.
Importance of Creating Habitats for Pollinators:
Biodiversity: Pollinators are vital for the reproduction of many plants. By supporting pollinators, you enhance the biodiversity and resilience of your garden.
Ecosystem Health: Pollinators help maintain the health of ecosystems by ensuring that plants reproduce. This not only benefits the immediate environment but also supports agriculture and food supply.
Plant Choices and Landscape Features that Attract Pollinators:
Diverse Plantings: Include a variety of plants that flower at different times of the year to provide a consistent source of food for pollinators.
Native Plants: Opt for native species that are more likely to attract local pollinators. Native plants generally provide the best nutrition and support for native wildlife.
Avoid Pesticides: Pesticides can harm pollinators. Using natural pest control methods, as discussed, ensures that your garden is safe for these beneficial creatures.
Specific Features to Enhance Pollinator Attraction:
Water Sources: Including features like birdbaths or shallow water dishes can provide necessary water for pollinators.
Shelter: Leave some areas of your garden a little wild to provide shelter for pollinators. Features like brush piles, old logs, and nesting boxes can make your garden more welcoming.

7. Sustainable Gardening Tools and Resources
Adopting eco-friendly gardening practices extends beyond plant and soil management to the very tools and resources we use. Selecting sustainable products not only minimizes environmental impact but also supports the overall health and longevity of your garden.
Choosing Tools Made from Sustainable Materials:
Biodegradable Planters: Opt for pots made from natural materials like coconut coir or rice husk, which decompose naturally without leaving harmful residues.
Recycled Tools: Consider gardening tools made from recycled materials. These tools reduce waste and the need for new resources, supporting a circular economy.
Wooden Tools: Tools with wooden handles from sustainably managed forests are a durable, eco-friendly choice that also have a lower carbon footprint compared to plastic alternatives.
Recommendations for Eco-Friendly Gardening Resources and Products:
Organic Fertilizers and Compost: Use products certified organic by reputable organizations. These fertilizers support soil health without the environmental downsides of synthetic fertilizers.
Natural Pest Control Solutions: As previously mentioned, opt for natural pest control products like neem oil or diatomaceous earth, which are effective yet gentle on the ecosystem.
Educational Resources for Sustainable Gardening:
Books and Guides: Seek out books and online guides dedicated to sustainable gardening techniques. Titles such as The Organic Gardener's Handbook offer a wealth of information.
Workshops and Webinars: Participate in workshops and webinars offered by local botanical gardens or environmental groups that focus on eco-friendly gardening practices.

Cultivating a Greener Tomorrow
As we embrace the principles of eco-friendly gardening, we not only enrich our own landscapes but also contribute to a healthier planet. Each choice we make—from the types of plants we nurture to the ways we manage our resources—has a profound impact on the environment. At Rolling Fields Tree Farm, we share your enthusiasm for plants, nature, and gardening, and we're excited to be a part of a community that values the beauty and sustainability of the natural world.
While we specialize in providing high-quality Arborvitae, which are ideal for privacy screens and sustainable landscaping, we also celebrate the broader aspects of gardening and environmental stewardship. Our passion for green spaces drives us to explore and share the many facets of gardening that can enhance our ecosystems and our lives.
Explore More with Rolling Fields
We invite you to delve deeper into the world of gardening with us. Check out our other blog posts on topics ranging from tree care to sustainability and home improvement. Each article is crafted to help you grow your knowledge and inspire your gardening projects.
And when you're ready to add beauty and privacy to your landscape with robust, evergreen trees, browse our selection of Arborvitae at greengianttrees.com. Join us in fostering greener spaces that not only look great but also do good for the environment.
Together, let's cultivate a greener tomorrow—one plant at a time.

.png)